Draw an oxygen dissociation curve & describe how oxygen is transported in the blood.What is the significance of sigmoid shape of the curve .
It is transported to the tissue capillaries in two forms-
1. Dissolved in the plasma- very small amount of O2
2. Combined with Hb- most of O2 (almost 200-300 times as much of dissolved state.)
- Transport of Oxygen in the dissolved state
– 0.3 ml of 02/ 100ml of blood in is present in dissolved state.
– 0.17 ml of O2 is normally transported to the tissues in dissolved state.”
-3% of the total
-97%transported in bonded form with Hb. - Role of Hb in oxygen transport:
– 97%. of total of transport.
– 15g of Hb in 100 ml of blood can combine expressed with total of about 20 ml of O₂ if the Hb is 100% saturated.
But, Hb is 97% saturated which is about 19.4 ml/100 ml of Blood. - under normal conditions, about 5 ml of O2 is transported from the lungs to the tissues. by each 100 ml of blood flow.
- Under strenuous exercise condition, 15 ml is the quantity of O2 actually delivered to the times. by each 100ml of blood flow.
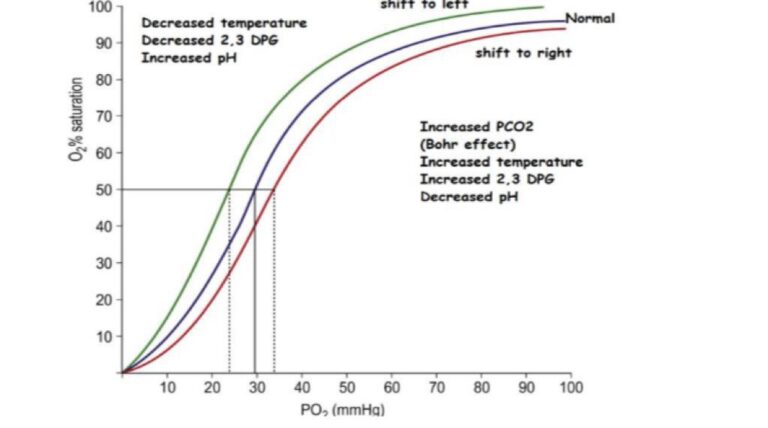
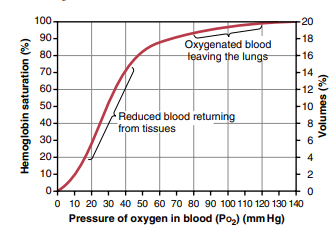
- The O₂ carrying power of Hb in given by oxygen- Hb dissociation curve ie. the curve relating percentage a saturation of the Hb to the PO₂.
Characteristic feature and Significance:-
• sigmoid or S-shaped
• Consists of two zones:
1. Loading zone refers to plateau (upper flat part)
– This is related to the process of O2 uptake in the lungs
– At PO2 of 100 mm Hg, the Hb is 97% saturated (Arterial blood)
2. Unloading (dissociation) zone refers to the steep portion of the curve at PO2 below 60 mm Hg
-concerned with O2 delivery in the tissues
-At PO2 of 40 mm Hg, the Hb is 75% saturated (venous blood)
Advantages of sigmoid shape of ODC
• Allows greater uptake of O2 at lungs inspite variation in alveolar PO2
• Tissues are supplied with O2 according to the needs of tissues
• Hb acts as a buffer for O2 & maintains tissue PO2 at 40 mm Hg.
Depict The Bohr's Effect and its significance?
Bohr’s effect refers to the phenomenon where the oxygen binding affinity of hemoglobin decreases when there is a decrease in pH or an increase in carbon dioxide concentration. This effect is important in regulating oxygen delivery to the tissues and has several significant physiological implications:
Promotes oxygen unloading: Bohr’s effect ensures that oxygen is released from hemoglobin in areas of high metabolic activity, where carbon dioxide and acidity are elevated. This allows the tissues to receive adequate oxygen supply despite increased demand.
Enhances gas exchange in the lungs: When blood reaches the lungs, the higher pH and lower carbon dioxide levels cause hemoglobin to have a higher affinity for oxygen. This promotes oxygen uptake in the lungs.
Helps regulate respiration: The changes in pH and carbon dioxide levels that affect Bohr’s effect are sensed by chemoreceptors in the body, which can stimulate changes in breathing rate and depth to maintain adequate oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
Supports exercise performance: During exercise, there is increased production of carbon dioxide and lactic acid, leading to a decrease in pH. The Bohr’s effect allows for increased oxygen delivery to the working muscles, which is important for exercise performance.
Overall, the Bohr’s effect plays an important role in regulating oxygen delivery to the tissues and maintaining acid-base balance in the body
What are the factors affecting o2 dissociation curve
- Factors influencing ODC(oxygen dissociation curve)
Several factors affect the affinity of Hb for O2 & shift the ODC either to right or left
Shifting of curve to right – Hypoxia
– Increase in PCO2
– Decrease in pH of blood (Accumulation of acidic products like lactic acid, CO2 etc.,)
– Increase in temperature
– 2, 3, DPG (diphosphoglycerate) –- Shifting of curve to left
– decreased PCO2 of blood
– increased pH of blood
– decreased temperature
– Fetal Hb - Effect of exercise on ODC
As exercise leads to increase in PCO2 (due to increase in metabolism), increase in pH (accumulation of acids) & increase in temperature (due to increase in metabolism), the ODC is shifted to right