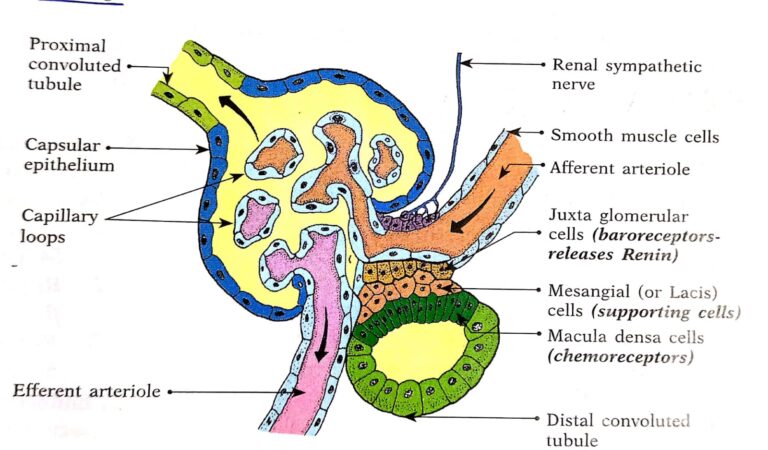
Write short note on Juxta Glomerular apparatus
The JGA is a combination of specialized tubular and vascular cells located at the vascular pole where the afferent and efferent arterioles enter and leave the glomerulus. It is composed of three cell types .
1. Juxtaglomerular cells (JG cells).
Before entering the glomerulus, the afferent arterioles show an asymmetrical thickening of its wall in the media. This contains ‘myoepithelial’ cells (modified vascular smooth muscle cells), called ‘JG cells. The JG cells have well developed golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum; abundant mitochondria and ribosomes. They synthesize, store and release a proteolytic enzyme, called renin. Renin is stored in granules of the JG cells.
(i) The JG cells are baroreceptors and respond to changes in the transmural pressure difference between the afferent arteriole and the interstitium. They are innervated by sympathetic nerve fibres.
(ii) These vascular volume receptors monitor renal perfusion pressure and are stimulated by hypovolemia or decreased renal perfusion pressure.
2. Macula densa cells (macula means spot; dense means crowded). These are specialized renal tubular epithelial cells located at the site where thick segment of ascending limb of loop of Henle is continued as DCT.
(i) These cells are in direct contact with the mesangial cells, in close contact with the JG cells, and adjoining with both the afferent and efferent arterioles.
(ii) These cells have prominent nuclei and function as chemoreceptors. They are stimulated by a decreased Na+ (NaCl) load thereby causing increased renin release.
(iii) These cells are not innervated, not well adapted for reabsorption and do not show signs of secretory activity.
3. Mesangial cells or Lacis cells-
These are supporting cells of JGA and found between capillary loops. They are in contact with both the JG cells and the macula densa cells.
(i) They are contractile and play a role in the regulation of glomerular filtration.
(ii) They show granulation to secrete renin in conditions of extreme hyperactivity.
(iii) They also secrete various substances and take up immune complexes.
The JGA regulates the renin secretion into the blood stream.
Normal plasma renin level: 200 ng/dL
Write short note on Glomerular filtration rate
Definition: The amount of filtrate that is formed by both the kidneys per minute is called glomerular filtration rate.
Normal value:
125 ml/minute
180 L/minute
Factors regulating GFR:
GFR-Kf x EFP (Kf-Filtration coefficient, EFP-Effective Filtration Pressure)
1. Kf – Filtration coefficient which denotes the efficiency of the filtering membrane to filter the plasma. This depends upon the following factors
A. Thickness of filtering membrane: Inversely proportional to Kf Increase in thickness reduces Kf and thereby reduces GFR also
B. Surface area of the membrane: Directly proportional to Kf & GFR
-the normal surface area is about 0.8 m²
-Contraction of the mesangial cells compresses the glomerulus & reduces the area of the membrane
C. Permeability of the membrane:
-Glomerular capillaries are 50 times more permeable than capillaries of skeletal muscle
-Permeability of the membrane is influenced by
- size of the particles filtered
- charge of the particles filtered
-Charge of the pores in the filtering membrane
- Particles below 4 nm size (both negative & positive charged) are filtered easily
- Particles above 8 nm size (both negative & positive charged) are not filtered
- Particles of 4-8 nm size are filtered with difficulty (Positively charged particles are filtered in this size range where as negatively charged particles are not filtered)
Reason: The negative charge of the pores in the filtering membrane repel the negatively charged particles
Eg-Albumin which is about 6 nm size is not filtered as it is negatively charged particle
2. Effective Filtration Pressure: It is the net outward pressure which determined by forces acting across the filtering membrane. These forces are called Starting forces
Starling Forces acting across the filtering membrane:
1. Glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure (PGC)= 45 mmHg (favors filtration)
2. Glomerular capillary osmotic pressure (πGC) = 25 mmHg (oppose filtration)
3. Bowmans capsular hydrostatic pressure (PBS) = 10 mmHg (oppose filtration)
4. Bowmans capsular osmotic pressure (πBS) = 0 (no effect on filtration)
EFP = Forces favoring filtration – Forces opposing filtration
EFP = PGC+πBS-PBS+ πGC
= (45 + 0) – (10 + 25)
= 10 mmHg
Thus GFR = Kf X EFP
= 12.5 x 10
=125ml / minute
Conditions which alter Starling’s forces:
Glomerular Hydrostatic pressure (PGC):
- Change in systemic blood pressure – directly proportional to PGC
- Constriction of afferent arteriole – decreases PGC
- Constriction of efferent arteriole increases PGC
Glomerular osmotic pressure (лGс):
i) Dehydration increases лGc
ii) Malnutrition – decreases лGc
Bowman’s capsular Hydrostatic pressure (PBS):
i) Ureteral obstruction – increases Pbs
ii) Edema of the kidney inside the tight renal capsule – increases Pbs
C) Renal blood flow:
– directly proportional to GFR. Renal blood flow is influenced by nerves, hormones like catecholamines, angiotensin, dopamine & ANP
D) Sympathetic stimulation:
strong acute sympathetic stimulation
↓
constriction of both afferent and efferent arterioles
↓
decrease in renal blood flow
↓
decrease in GFR
Write short note on regulation of GFR
REGULATION OF GFR
- Autoregulation
- Mesangial cells
#Autoregulation mechanism:-
1. Myogenic mechanism
stretching of vessel wall
↓
↑ movement of Ca++ion from ECF to vascular Smooth muscle cells
↓
Combines with calmodulin and activation of myosin cross bridges
↓
RBF restore
↓
GFR restore
2. TUBULOGLOMERULAR FEEDBACK
Tubuloglomerular feedback refers to a mechanism which maintains a constant renal blood flow & GFR inspite of the changes in mean arterial pressure. It involves the feedback signals from DCT when there is a change in the concentration of sodium chloride in the tubular fluid
Increased renal arterial pressure
↓
Increased RBF & GFR(-)←←←←←←←←←←←←←←←←←←
↓ ↥
Increased NaCl concentration In the tubular fluid ↥
↓ ↥
Sensed by macula densa cells ↥
↓ ↥
Feedback effect (Release of adenosine) ↥
↓ ↥
Constriction of afferent arteriole ⟶⟶⟶⟶⟶⟶⟶ ↥
Decreased renal arterial pressure
↓
Decreased RBF & GFR(-)←←←←←←←←←←←←←←←←← ↥
↓ ↥
Decreased NaCl concentration in the tubular fluid ↥
↓ ↥
Sensed by macula densa cells ↥
↓ ↥
Feedback effect ↥
(Less release of adenosine) ↥
↓ ↥
Dilation of afferent arteriole⟶⟶⟶⟶⟶⟶⟶⟶⟶ ↥
3 High protein diet → ↑ GFR ?
↑↑↑Amino acids
↓
PCT: Na, AA reabsorption ↑↑ (coupled reabsorption)
↓
↓Nacl reaches DCT
↓
Macula Densa & JG cells
↓
↑GFR
#Mesangial cells
Cells surrounding glomerular capillaries
CASE 1:
constriction of macula densa cells
↓
compresses glomerular capillary
↓
less blood through glomerular capillaries
↓
↓GFR
Agents responsible for constriction of macula cells:
-Endothelin
-Angiotensin
-Nor-epinephrine
CASE 2:
Dilation of macula densa cells(relaxation)
↓
expands glomerular capillaries
↓
more blood through glomerular capillaries
↓
↑GFR
Agents responsible for relaxation of macula densa cells:
–nitric oxide
-natriuretic peptide
-dopamine
-cAMP

